GEODETIC & GEOPHYSICAL SENSORS
Gravity Measurement

Measuring Earth's gravitational field
The strength of Earth’s gravitational field varies with the mass distribution of the Earth’s surface. A gravimeter measures these gravitational variations for applications in geophysical surveying, including oil and mineral exploration, underground fluid monitoring, and mapping terrain. Such sensors may also be utilized for geodetic studies of Earth’s gravitational potential, identifying special nuclear materials, treaty verification, and void detection.
GRAVIMETERS & GRADIOMETERS
Atom interferometry and gravitation
Precise measurement of changes in Earth’s gravitational field is technically challenging. Atom-based measurement methods are exceptionally sensitive to these changes. An atom gravimeter utilizes cold atoms, laser beams, and wave-particle duality to measure the gravitational acceleration of the earth. A gravity gradiometer detects very small gravitational fluctuations.
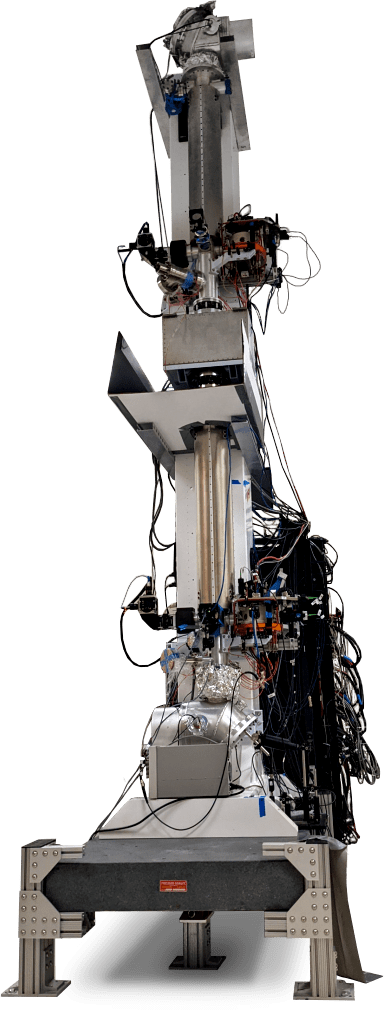
AOSENSE GRAVITY SENSORS
Cold-atom gravity sensors
AOSense has built and demonstrated cold-atom sensors for measuring gravity and gravitational gradients, including an atom-optics gravity gradiometer. This compact and efficient sensor, which utilizes two gravimeters with cold atoms falling at different heights, produces a highly accurate gravity gradient. Read more about it here.
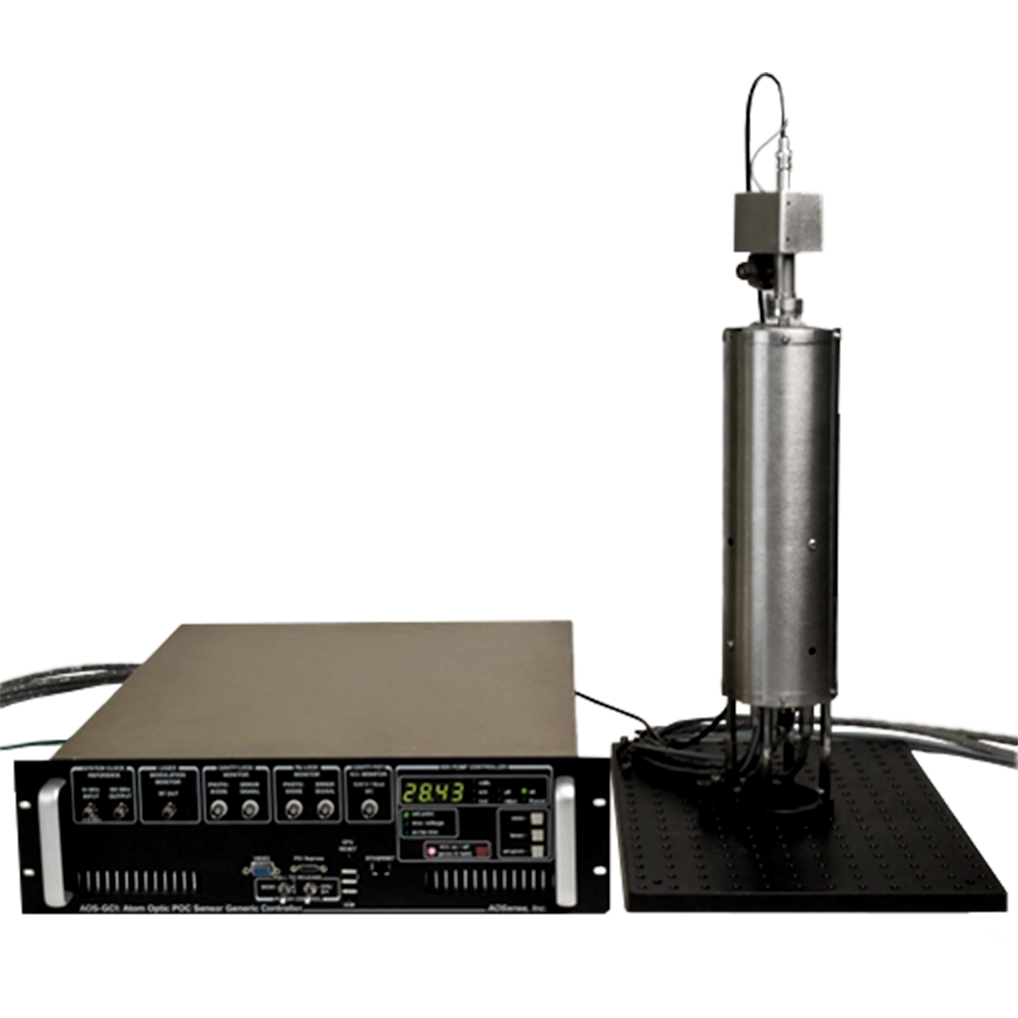
AOSENSE GRAVIMETER
Compact gravimeter
In 2010, AOSense built and sold a compact high-performance gravimeter for an aerospace customer. The AOSense compact gravimeter integrates an entire lab of equipment into a portable sensor head and controller, incorporating all necessary lasers, vacuum, and electronics to cool, control, and readout the atomic test masses. The sensor is capable of operating autonomously and acquiring data for weeks.

